Understanding Shoulder Rotation Issues: Causes and Solutions

The human body is a complex system, and the shoulder joint is one of the most intricate components. As individuals engage in daily activities, they might encounter various musculoskeletal issues, one of which is being unable to externally rotate the shoulder. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options for this condition.
The Anatomy of the Shoulder Joint
To understand the implications of shoulder rotation issues, it's important to grasp the basic anatomy of the shoulder joint. The shoulder consists of three main bones:
- Humerus
- Scapula (Shoulder Blade)
- Clavicle (Collarbone)
These bones come together to form a ball-and-socket joint, which allows for a wide range of motion. Various muscles and tendons, including the rotator cuff, provide stability and mobility, enabling activities such as lifting, throwing, and reaching.
What Does It Mean to Be Unable to Externally Rotate the Shoulder?
When someone is unable to externally rotate the shoulder, they are experiencing restrictions in the usual range of motion. External rotation is critical for numerous overhead activities, including sports, lifting, and daily tasks. Understanding the limitations caused by this deficiency is essential for pinpointing the source of the problem.
Symptoms Associated with Limited External Rotation
Individuals may experience a variety of symptoms when facing this condition, including:
- Pain during certain movements.
- Tightness in the shoulder region.
- Weakness in the shoulder muscles.
- Instability or a sensation that the shoulder could dislocate.
- Limited range of motion, especially when trying to lift the arm.
Causes of Inability to Externally Rotate the Shoulder
Understanding the root causes of being unable to externally rotate the shoulder is crucial for effective treatment. Several factors can contribute to this issue:
1. Rotator Cuff Injuries
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder. Injuries to this area, such as tears or tendinitis, can limit movement and cause pain, making it difficult to achieve external rotation.
2. Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
This condition occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff become irritated and inflamed. Activities that involve overhead lifting or repetitive shoulder movements can lead to this syndrome, resulting in pain and restricted motion.
3. Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Frozen shoulder is characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint. The capsule surrounding the shoulder becomes thick and tight, significantly reducing the range of motion, including external rotation.
4. Arthritis
Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can lead to inflammation in the joint, causing pain and decreased mobility. This can affect the shoulder's ability to rotate externally.
5. Muscle Imbalances
Imbalances in shoulder muscles, particularly between the internal and external rotators, can affect motion and stability, contributing to difficulties in external rotation.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Rotation Issues
Diagnosing the cause of being unable to externally rotate the shoulder involves a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional. The process typically includes:
- Medical History Review: Discussing symptoms, previous injuries, and activity levels.
- Physical Examination: Assessing the range of motion, strength, and pain levels.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds may be utilized to visualize the shoulder structures and identify any abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Rotation Limitations
Treating issues related to being unable to externally rotate the shoulder requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment strategies:
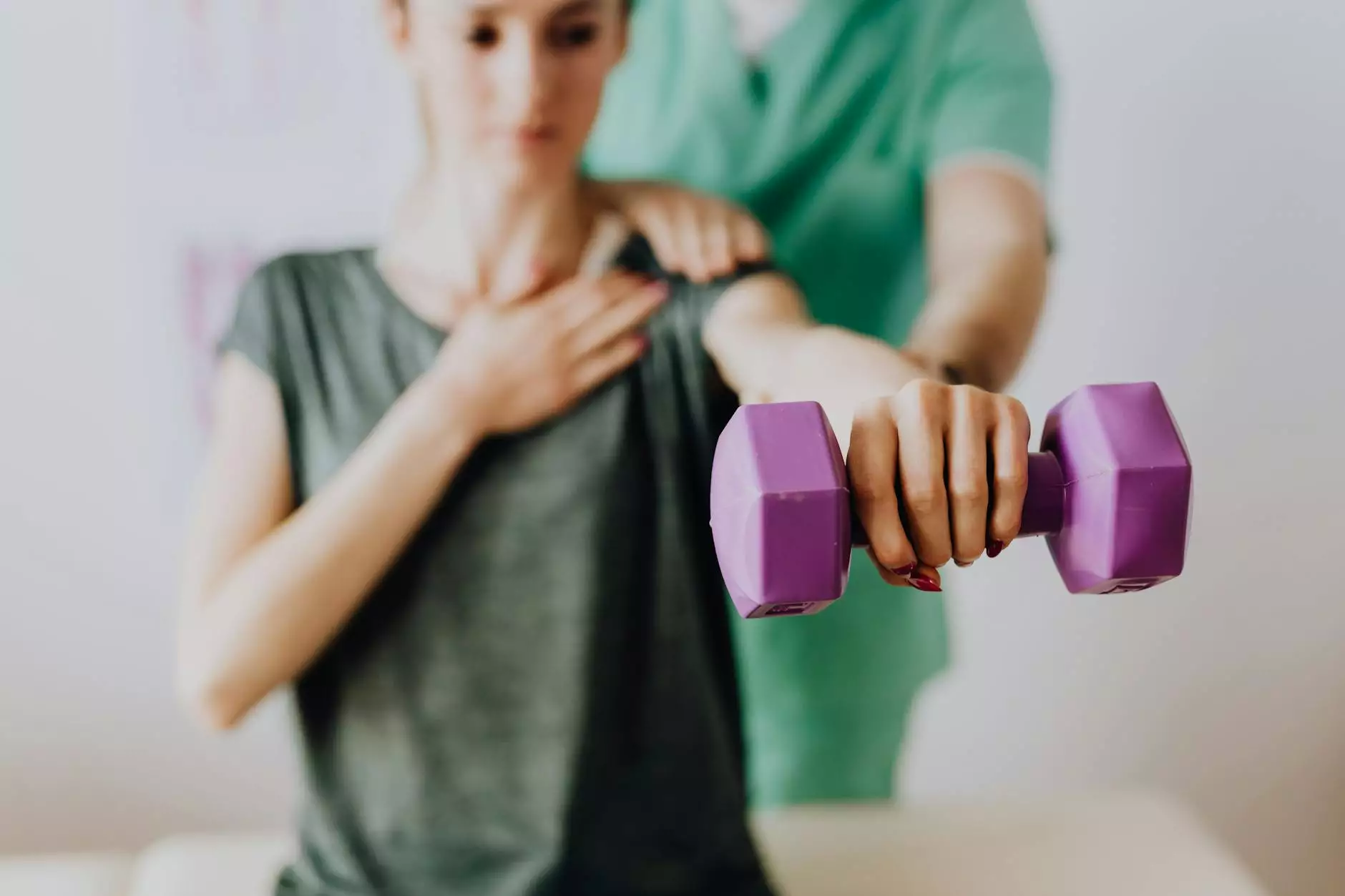
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a critical role in rehabilitation. A physical therapist can design a personalized program to:
- Improve flexibility.
- Strengthen shoulder musculature.
- Restore range of motion.
Exercises may involve stretching, strengthening, and functional movement training.
2. Medication
Over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen), can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide more immediate relief.
3. Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the shoulder and modifying activities to avoid aggravation is essential for recovery. This might involve using assistive devices or avoiding overhead lifting until mobility improves.
4. Surgical Options
In cases where conservative treatments do not provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures such as arthroscopy can help repair damaged tendons, relieve impingement, and liberate adhesions in frozen shoulder cases.
Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive measures can help prevent issues related to shoulder rotation limitations:
- Regular Strength Training: Focus on shoulder stability exercises that strengthen the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles.
- Flexibility Work: Incorporate stretching routines for the shoulders and upper back to maintain optimal range of motion.
- Avoid Overuse: Be cautious with repetitive overhead activities and ensure proper techniques when engaging in sports or weightlifting.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Make ergonomic changes in work and daily life to minimize shoulder strain.
Conclusion
In summary, being unable to externally rotate the shoulder is a condition affecting many individuals, stemming from a variety of causes. Understanding the underlying issues, seeking appropriate treatment, and embracing preventative strategies are essential steps toward recovery. For those experiencing shoulder rotation difficulties, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a tailored treatment plan. By taking proactive measures and being mindful of shoulder health, individuals can maintain optimal function and enjoy an active lifestyle.
For more resources on shoulder health and rehabilitation, visit iaom-us.com.
unable to externally rotate shoulder